RAID 0 Data Recovery
RAID 0, the lowest level of RAID, is one of the simplest RAID configurations. It provides the greatest boost in performance. But it is also the RAID level with the least amount of fault tolerance and data protection, meaning that in the event of failure, an expert could be needed to recover data from the array. At Gillware, we offer financially risk-free RAID 0 data recovery services.
Free in-lab RAID 0 Recovery Evaluation
Our data recovery company always starts with a free evaluation of your data loss situation. There are no upfront fees for any part of our data recovery services. We even offer to cover the cost of inbound shipping. With a prepaid UPS shipping label, you can send your crashed RAID 0 array to us at no cost.
Our RAID 0 data recovery engineers will take and assess every drive in the array. We send you a statement of work to recover data based on the amount of damage, data loss, and the number of drives in the array. After data recovery evaluation, we know enough to present you with a firm price quote, estimated time to recover files, and probability of data recovery success. If the terms of our RAID 0 data recovery process are not to your liking, you are free to back out without paying us a dime.
A failed RAID 0 will keep you from your critical data.

Independent Analysis of Your RAID 0 Array’s Hard Disks
Each healthy drive is completely copied over to one of our secure internal customer data disks. Our custom-designed RAID recovery software, HOMBRE, makes full forensic write-blocked drive images for analysis. At no point do we ever perform forensic data recovery analysis on a customer’s original drive, or alter the RAID 0 data files on the drive. We repair all the member disks as needed using spare parts and our data recovery software. Our RAID 0 recovery engineers work hard to get as many of the failed RAID 0 member disks imaged using our data recovery software/disk viewer tool as possible.
The RAID controller places special metadata on each drive in the array. Using RAID 0 data recovery software, our engineers identify and analyze this metadata to determine how the data fits together in the array. Our RAID 0 recovery computer scientists write custom RAID recovery software to arrange our images of the array’s hard disks. If any data is missing, our technicians work around the holes to give you the best RAID recovery results possible.
When we recover RAID 0 data, a data recovery specialist will make certain that your critical data and files are as functional and uncorrupted as possible before we send you our bill. If necessary, we show you a list of recovered files so you can help us determine whether or not our data recovery efforts are successful. If we are unable to recover data you need from your RAID 0, you owe us nothing for RAID 0 data recovery. The entire RAID recovery process is financially risk-free.
Reuniting You with Your Data
We send your files and data back to you after your RAID recovery has been completed and paid for. We never hold on to your recovered files for very long. In the interest of security, we wipe all of your recovered data from our internal customer data drives after you have had a chance to verify that your recovered data works. Normally, we hold onto RAID 0 data for five business days after you receive your files. Then, we securely erase your files using our drive sanitizer.
What Is RAID 0?
The bigger your data storage needs, the more hard disks you need. But it’s awfully inconvenient to have a dozen separate hard drives storing your data. Fortunately for you, there’s a way to take those dozen hard drives and make them act like one giant hard drive. This is called a redundant array of independent disks, or RAID.
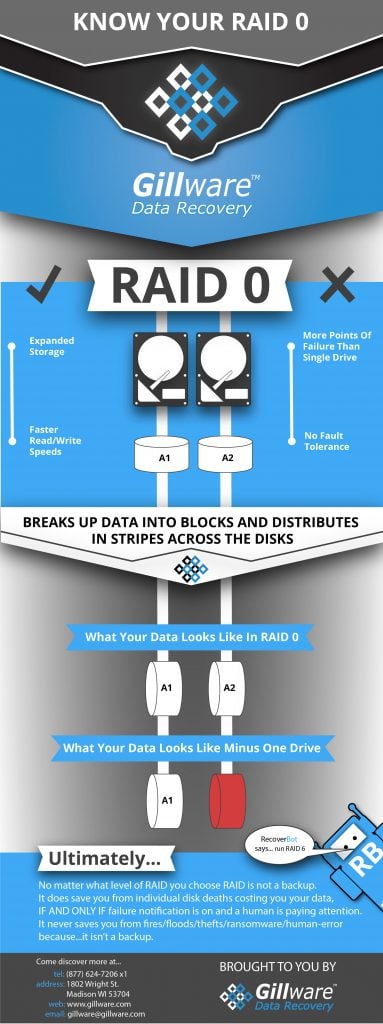
RAID 0 is commonly used by home users, and with two hard disks, also called member disks. A two-drive RAID 0 array is more than twice as fast as a single hard drive on its own, since it can perform multiple read/write operations simultaneously. RAID 0 generally suffers from diminishing returns the more member disks there are in the array, though, so people with three or four drives or more are likely to use higher RAID levels with other features and benefits.
You can visit our article on RAID 0 for a more detailed explanation of this RAID configuration.
How RAID 0 Arrays Work
To make a RAID 0 array, you take your member disks and stick them together. Whenever you write data to your RAID array, the data gets split up into blocks and divvied up among the drives in the array. This is called disk striping. Each block or stripe is usually 64 kilobytes. Every hard drive in the array is used to its full capacity. If you have three 8-terabyte Western Digital drives in a RAID 0 array, you have 24 terabytes of storage space.
Now, say you have your three-drive RAID 0. You want to write a 640-kilobyte file to the array. That RAID controller breaks it into 10 64-kilobyte blocks. (If the file were 653 KB, you’d have eleven blocks, with the last thirteen kilobytes in the eleventh one.) These 10 stripes go to the drives in the RAID-0. Drive 0 gets the first stripe. Drive 1 gets the second. Drive 2 gets the third. Drive 0 gets the fourth. And so on and so forth.
Later on, you open up your file. A single hard drive has to read each block containing the parts of your file one at a time. But in your RAID 0 array, all of the drives are working together, and you can read up to three data blocks simultaneously. Your three-drive RAID 0 array won’t be exactly three times faster than a single hard drive. But it will be noticeably faster than one hard drive on its own.
Talk to RAID 0 Data Recovery Expert Today!

Our RAID 0 recovery client advisors are available by phone during business hours
(M – F: 8am – 7pm; Sat: 10am – 3pm).

Send us an email if you need a RAID recovery expert to help you recover data. A client advisor will respond within 25 minutes during business hours
(M – F: 8am – 7pm; Sat: 10am – 3pm).

Have a quick question about data recovery from RAID? Use our chat feature to chat with one of our data recovery client advisors (not a robot!) during business hours
(M – F: 8am – 7pm; Sat: 10am – 3pm).

Want to schedule a call for a time that is convenient for you? Click the button above to schedule a brief RAID data recovery consultation with one of our client advisors.
Click here to schedule a call
RAID 0’s Shortcomings
RAID 0 seems great if you’re a speed demon. Every drive in the array increases your storage space and boosts your read/write speeds. But there’s a catch.
Other RAID levels, like RAID 1, RAID 5, RAID 6, and RAID 10, use up some of their drives’ storage capacity to provide data redundancy. If one of the member disks fails, there’s at least one other drive to step in. These RAID levels sacrifice some efficiency and storage space for fault tolerance.
But RAID 0 makes no compromises in its pursuit of speed, making these arrays likely to fail. But if you are a speed demon, you shouldn’t be using spinning disk media anyway: Solid-state drives are much faster and are becoming more affordable every year.
Take another look at your three-drive RAID 0. Imagine one of the three drives stops working. There’s a lot of reasons why a member disk failure could happen. Maybe there was a power loss. Or the drive’s read/write heads wore out. Or the drive’s firmware got a bug. There are a lot of different ways member disks can fail. If you’re very unlucky, a disaster might cause more than one drive to fail at once.
Now, one out of every three data stripes across your RAID 0 array is missing. This doesn’t mean that one out of three files on your array show as deleted files. Instead, the larger a file is, the more “holes” it will have. Parts of the file definitions and filesystem metadata will be gone as well. No matter how many drives you have in your RAID 0 array configuration, it only takes one failure to bring all the data down.
If your RAID storage solution uses the same model of hard drive, experiencing multiple drive failures in a short period of time is more likely than you may think. Consider the previous example with the three Western Digital 8TB hard drives. If you bought all three of those drives at the same time, they are very likely near-duplicates. Those drives may have come off the assembly line minutes or seconds apart. With those three drives in a RAID 0 system, they will be performing nearly identical read / write operations. As such, it is well within the realm of possibility that one, two, or even all three of these drives could suffer mechanical failure around the same time.
Whoever coined the ancient proverb “A chain is only as strong as its weakest link” wasn’t talking about data loss on a failed RAID 0. But they might as well have been.
Your data is more at risk in a RAID 0 array than any other type of RAID array configuration. In fact, our CEO Brian Gill doesn’t even consider RAID 0 to be a true RAID at all, since it offers a negative amount of redundancy. A two-drive RAID 0 is actually more than twice as likely to crash as a single drive, because not only have you doubled your chance at drive failure, but a RAID controller failure is possible as well. Controller failures can make the entire array, and with it, the entire data storage device, inaccessible.
Looking for a different type of data recovery?

If you would like to contact us to receive a no-pressure consultation to recover files, click the button below. This will take you to a page with our phone number and email. This page also provides you with the option to schedule an appointment with a Client Advisor at a later time or date, or chat with them online.
Click the button below if you would like to send in your device. Sending in your device is financially risk-free. You will be asked to fill out a short form. Once you have completed the form, we will send a shipping label to the address provided. After we receive your device, a data recovery specialist will begin a free evaluation and contact you with a firm price quote.
